
In the realm of civil engineering and construction, ensuring the proper compaction of materials such as soil, asphalt, and concrete is crucial for the longevity and stability of structures. This meticulous process is facilitated by a vital tool known as the density testing gauge. This guide aims to delve deeply into the workings, applications, and significance of density testing gauges in modern construction practices.
What is a Density Testing Gauge?
A density testing gauge, often referred to simply as a density gauge, is a specialized instrument used to measure the density and moisture content of compacted materials. It plays a pivotal role in quality control during construction projects, ensuring that materials are compacted to specified standards. The gauge provides valuable data that helps engineers and technicians assess whether the compaction process has achieved the desired level of density, which directly impacts the structural integrity and performance of the finished infrastructure.
Components and Operation
Density testing gauges typically consist of several key components:
- Radioactive Source: Many density gauges utilize a small, encapsulated radioactive source, such as Cesium-137 or Americium-241. This radioactive source emits gamma radiation into the material being tested.
- Detector: The gauge also contains a detector that measures the amount of gamma radiation that is either absorbed or scattered back to the gauge. This measurement is directly related to the density of the material.
- Display and Controls: Modern density gauges often include a digital display that provides immediate readings of density and moisture content. They may also feature controls for calibration and data storage.
Applications in Construction
Density testing gauges find widespread use across various construction disciplines:

- Road Construction: Ensuring proper compaction of soil and asphalt layers is critical for road durability and load-bearing capacity.
- Building Foundations: Properly compacted soil beneath building foundations prevents settling and structural issues over time.
- Landfills: Compacted waste materials in landfills help minimize volume and prevent environmental contamination.
Types of Density Testing Gauges
Density gauges can be broadly categorized into two types based on their operation:
- Nuclear Density Gauges: These gauges use a radioactive source to emit gamma radiation into the material. The amount of radiation detected correlates with the density of the material. They are highly accurate and widely used despite the need for regulatory compliance and safety protocols.
- Non-Nuclear Density Gauges: Developed as alternatives to nuclear gauges, these instruments use technologies such as neutron scattering or electromagnetic waves to measure density and moisture content. They offer the advantage of being non-radioactive, thus simplifying regulatory requirements and safety procedures.
Importance of Calibration and Maintenance
For density testing gauges to provide accurate and reliable measurements, regular calibration and maintenance are essential. Calibration ensures that the gauge accurately interprets the readings of gamma radiation or other measurement signals. Proper maintenance, including periodic checks and servicing, helps extend the lifespan of the gauge and ensures consistent performance on-site.
Safety Considerations
Due to the presence of radioactive materials in nuclear density gauges, strict safety protocols must be followed:
- Training: Operators must undergo specific training on gauge operation, safety procedures, and regulatory compliance.
- Shielding and Containment: Gauges are designed with shielding to contain the radioactive source and prevent radiation exposure to operators and the public.
- Regulatory Compliance: Operators must adhere to local regulations regarding the use, transport, storage, and disposal of radioactive materials.
Advancements in Technology
Recent advancements in technology have enhanced the capabilities of density testing gauges:
- Integrated GPS: Some modern gauges feature integrated GPS technology, allowing for precise location tracking and mapping of density measurements across construction sites.
- Wireless Connectivity: Wireless data transfer capabilities enable real-time monitoring and remote access to measurement data, enhancing efficiency and project management.
- Data Analytics: Advanced gauges may include built-in data analytics software that provides insights into compaction trends, material characteristics, and project progress.
Environmental and Economic Impact
Proper compaction, facilitated by density testing gauges, offers significant environmental and economic benefits:
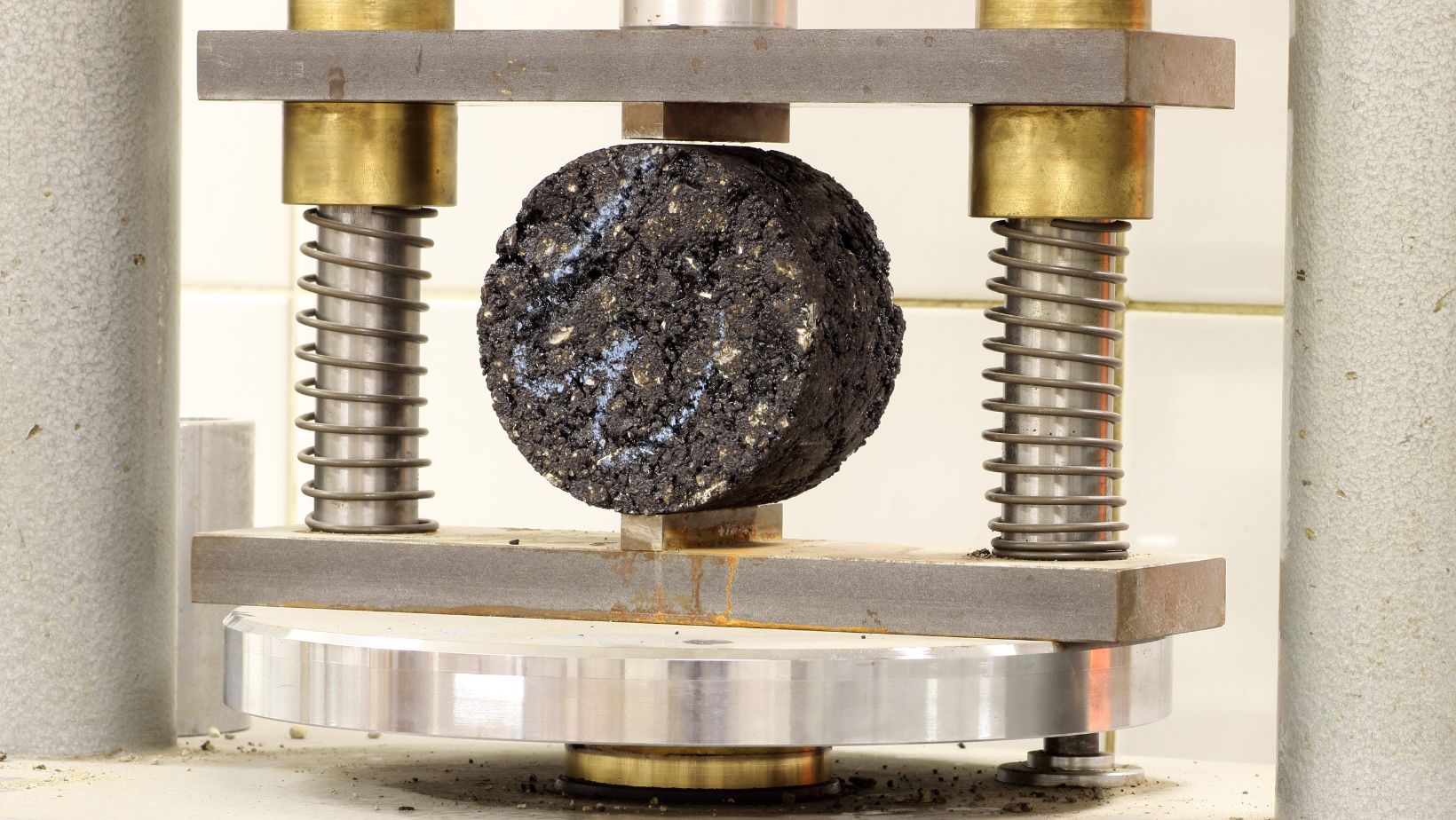
- Resource Efficiency: Optimal compaction reduces material usage and waste, contributing to sustainable construction practices.
- Long-Term Durability: Well-compacted materials result in infrastructure that requires fewer repairs and replacements over its lifespan, reducing lifecycle costs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, density testing gauges are indispensable tools in the construction industry, ensuring that materials are compacted to specified standards for optimal structural integrity and performance. As technology continues to evolve, these gauges are becoming more sophisticated, offering enhanced capabilities and efficiencies. However, it is crucial to emphasize the importance of safety and regulatory compliance when using nuclear density gauges. By leveraging these instruments effectively, engineers and construction professionals can build infrastructure that is durable, sustainable, and resilient to environmental challenges.
Density testing gauges remain at the forefront of modern construction practices, driving innovation and excellence in the built environment. Their role in quality assurance and quality control underscores their importance as foundational instruments in the pursuit of safe, efficient, and sustainable construction projects worldwide.










